Methylprednisolone
A glucocorticoid.
General information
Methylprednisolone is a corticosteroid with immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities. It acts on nuclear receptors, which results in a decrease of proinflammatory cytokine production (NCIt). It has been used to study the effects on COVID-19 patients for its potential to impede the progress of pneumonia and to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome (Wang et al., 2020).
National Institute of Health COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel recomands the use of Methylprednisolone where Dexamethasone is not available (As of August 18th, 2020).
The WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19 published on September 4, 2020, issued a strong recommendation for systemic corticosteroids in patients with severe and critical COVID-19, and a weak or conditional recommendation against systemic corticosteroids in patients with non-severe COVID-19. The suggested regimen consists of dexamethasone (6 mg, oral or intravenous, daily for 7-10 days), and acceptable alternative regimens are hydrocortisone (50 mg, intravenous, every 8 hours for 7-10 days), methylprednisolone (10 mg, intravenous, every 6 hours for 7-10 days) or prednisone (40 mg, oral, daily for 7-10 days).
Methylprednisolone on DrugBank
Methylprednisolone on PubChem
Methylprednisolone on Wikipedia
Marketed as
DEPO-MEDROL; HYBRISIL; MEDRATE; MEDRONE; MEPROLONE; MEDROL; MEDROLOAN SUIK; METHYLPREDNISOLONE; METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE; METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE; SOLOMET; SOLU-MEDROL; URBASON
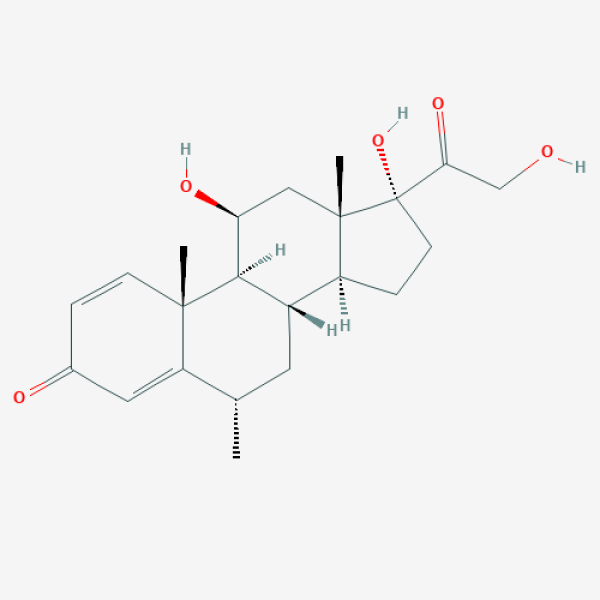
C[C@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@@]([C@]3(C[C@@H]([C@@H]2[C@@]4(C1=CC(=O)C=C4)C)O)C)(C(=O)CO)O
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Key to successful treatment of COVID-19: accurate identification of severe risks and early intervention of disease progression
Preprint |
Patients | Appropriate dose of methylprednisolone can effectively avoid invasive mechanical ventilation and reduce case fatality rate in critical COVID-19 patients |
Apr/11/2020 | |
|
COVID-19: disease pathways and gene expression changes predict methylprednisolone can improve outcome in severe cases
Severe severity Preprint |
in silico | May/19/2020 | ||
|
A Retrospective Controlled Cohort Study of the Impact of Glucocorticoid Treatment in SARS-CoV-2 Infection Mortality
|
Patients | 4.90 | survival of patients with SARS-CoV2 pneumonia is higher in patients treated with glucocorticoids than in those not treated |
Aug/20/2020 |
|
Effects of Anticoagulants and Corticosteroids therapy in patients affected by severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
Severe severity Preprint |
Patients | Early use of a combined anti-inflammatory (corticosteroids and Enoxaparin) and antiviral drugs treatment in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia prevent complications of the disease and improve clinical outcomes |
Jun/29/2020 | |
|
Prolonged Low-Dose Methylprednisolone in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
Severe severity Small molecule Non-randomized controlled open trial |
Severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients | 3.66 | Early low-dose prolonged treatment was associated with significantly lower risk of death and decreased dependence on mechanical ventilation. Improvements in systemic inflammation and oxygenation were observed, as well. Sample size: 83 + 90 control. Dosage: 80 mg IV loading dose; 80 mg daily in a continuous infusion until clinical improvement (for at least 8 days); 16 mg orally or 20 mg IV twice daily until further improvement in inflammation and oxygenation. Endpoint: Need for ICU referral, intubation, or death within 28 days composite (primary). |
Sep/12/2020 |
|
Tocilizumab and steroid treatment in patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia.
Severe severity Preprint |
Patients | Early adjunctive treatment with tocilizumab, methylprednisolone or both may improve outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia |
Jun/26/2020 | |
|
Initial experience with short-course corticosteroids in a small cohort of adults with severe COVID-19 in a tertiary care hospital in India
Severe severity Preprint Cohort study |
Patients | use of methylprednisolone in a dose of 30 mg twice daily was associated with rapid improvement in oxygenation and decline in CRP levels |
Jun/24/2020 | |
|
Therapeutic response to corticosteroids in a critically ill patient with COVID-19
|
Patient | 1.55 | A case report of clinical improvement and improvement of radiological findings in a critically ill patient after short-duration moderate-dose corticosteroid treatment. Dosage 80 mg twice a day for 3 days, then 40 mg twice a day for the following 3 days. |
Jul/16/2020 |
|
Glucocorticoids improve severe or critical COVID-19 by activating ACE2 and reducing IL-6 levels
|
GES1 cells; M0 and M1 macrophages | 4.86 | In vitro manifests ACE2 agonist activity and decreases IL-6 secretion in M1 macrophages. Theoretical amelioration of ACE2 depletion by virus attachment. |
Jun/27/2020 |
|
Glucocorticoids improve severe or critical COVID-19 by activating ACE2 and reducing IL-6 levels
|
Patients | 4.86 | Medium to small methylprednisolone doses might decrease inflammation in patients in severe to critical conditions. Sample size 9 patients. Dosage 40 mg/d if body weight ≤ 80 kg for the first 3-4 days, and then 20 mg/d for the next 3 days or more with a total of less than 8 days. If body weight is over 80 kg, 80 mg/d for 3-4 days and 40 mg/d for the next 3 days or more with a total of less than 8 days. Endpoints - IL-6 levels; lymphocyte count; CRP; CT findings. |
Jun/27/2020 |
|
Corticosteroid prevents COVID-19 progression within its therapeutic window: a multicentre, proof-of-concept, observational study
Small molecule Cohort study |
Patients | 5.78 | Patients in the early phase of excessive inflammation could benefit from short-term low to moderate corticosteroid treatment if their lactate dehydrogenase levels are less then two times the upper limit of normal. Sample size: 311+187 validation cohort. Dosage: 40–80u2005mg/d (0.75–1.5u2005mg/kg/d) of methylprednisolone for 3 days, then was tapered to 20u2005mg/d, with a total treatment period of less than 7 days. Endpoints: Requirement of invasive mechanical ventilation; adverse effects. |
Aug/21/2020 |
|
Tocilizumab and steroid treatment in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia
IL-6 Small molecule Antibody Cohort study |
Patients | 2.74 | Early methylprednisolone treatment (optionally in combination with tocilizumab) may improve clinical outcomes in non-intubated COVID-19 patients. Sample size: 45 + 56 with tocilizumab + 66 control. Dosage: 1 mg/kg for 5 days (+ optionally tocilizumab 8mg/kg intravenously or 162mg subcutaneously). Endpoint: Intubation/death-free survival. |
Aug/20/2020 |
|
High dosage of methylprednisolone as a rescue, second-line treatment in COVID-19 patients who failed to respond to tocilizumab
Severe severity Small molecule Case series Moderate severity |
Patients | 16.10 | Rapid and significant clinical improvement in pacients who failed to respond to azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine and two doses of tocilizumab treatment. Sample size: 5. Dosage: 1.5 mg/kg. |
Aug/19/2020 |
|
GLUCOCOVID: A controlled trial of methylprednisolone in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia
Preprint Randomized controlled open trial |
Patients | beneficial effect on the clinical outcome of severe COVID-19 pneumonia, decreasing the risk of the composite end point of admission to ICU, non-invasive ventilation or death |
Jun/18/2020 | |
|
Outcome of early-stage combination treatment with favipiravir and methylprednisolone for severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 11 cases
Severe severity Small molecule Case series |
Patients | 1.85 | Early treatment (in combination with favipiravir) in severe COVID-19 may prevent disease progression. Sample size: 11. Dosage: 80 (initial), 250, or 500 mg/day for 3–6 days. |
Aug/28/2020 |
|
Intravenous methylprednisolone pulse as a treatment for hospitalised severe COVID-19 patients: results from a randomised controlled clinical trial
Severe severity Small molecule Randomized controlled single-blind trial |
Patients | 12.34 | Severe COVID-19 patients treated with methylprednisolone pulse at the onset of the pulmonary phase of the disease showed shorter time to clinical improvement and lower mortality rate compared to the control group. Sample size: 34 + 28 control. Dosage: IV 250u2005mg/day for 3u2005days. |
Sep/17/2020 |
|
The role of methylprednisolone on preventing disease progression for hospitalized patients with severe COVID‐19
Severe severity Small molecule Cohort study |
Patients | 3.48 | Early methylprednisolone low to medium dosage treatment of severe COVID-19 patients younger than 65 years old significantly reduced progression to critical severity and mortality. No statistically significant differences were observed in older patients. Sample size: 175. Dosage: 50u201080 mg daily. |
Sep/20/2020 |
|
Second week methyl-prednisolone pulses improve prognosis in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia: An observational comparative study using routine care data
Severe severity Small molecule Cohort study |
Patients | 2.74 | COVID-19 patients with high inflammation and compromised respiratory functions (unlike those without respiratory compromise) significantly benefited from week-2 pulse methylprednisolone treatment when compared to non-week-2 scheme of methylprednisolone treatment or no methylprednisolone administration at all. Sample size: 61 (week-2 methylprednisolone) + 33 (other than week-2 methylprednisolone) + 148 (no methylprednisolone). Dosage: 125-250 mg daily for 3 days during the second week of COVID-19. Endpoints: Time to death and time to death or endotracheal intubation. |
Sep/22/2020 |
|
Early, low-dose, short-term methylprednisolone decreased the mortality in critical COVID-19 patients: A multicenter retrospective cohort study
Small molecule Critical severity Cohort study |
Critical patients | 4.84 | Patients with critical (but not those with less severe) COVID-19 benefited (60-day mortality) from short-therm low-dose (but not high dose) treatment with methylprednisolone. Sample size: 174 + 164 control. Dosage: No more than 80 mg daily for no more than 7 days. |
Nov/08/2020 |
|
Comparison of efficacy of dexamethasone and methylprednisolone in moderate to severe covid 19 disease
Severe severity Small molecule Moderate severity Cohort study |
Patients | 1.50 | Marked improvement in supplementary oxygen requirement, temperature, and CRP. Equally effective as dexamethasone in moderate to severe COVID-19. |
Nov/10/2020 |
|
Anakinra combined with methylprednisolone in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation: an observational cohort study
IL-6 Severe severity Small molecule Critical severity Antibody Cohort study |
Patients with hyperinflammation | 10.23 | In combination with anakinra. The treatment group patients with COVID-19-linked hyperinflammation were in a significantly lower adjusted and unadjusted risk of death compared to a historical control. Sample size: 65 + 55 control. Dosage: 1 mg/kg loading dose; 0.5 mg/kg twice daily on days 1-5; 0.25 mg/kg twice daily on days 6-10; 0.25 mg/kg daily (optionally divided into two doses) on days 11-14. Endpoint: 28-day mortality. |
Nov/18/2020 |
|
High‐Dose Methylprednisolone in Nonintubated Patients with Severe COVID‐19 Pneumonia
Severe severity Small molecule Cohort study |
Non-intubated patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia | 3.48 | Patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia not intubated at the baseline were in a significantly lower risk of mechanical ventilation and mechanical ventilation or death composite when treated with methylprednisolone compared to the control. These patients had in average more ventilator- and ICU-free days. 28-day mortality was not significantly different between the groups, however. Sample size: 153 + 294 control. Dosage: 1.78 mg/kg (median) full dose for 5 days (median), for 10 days total, including deescalation (median). Endpoint: Death or mechanical ventilation by the day 28 (primary). |
Nov/20/2020 |
|
Intravenous Immunoglobulin Plus Methylprednisolone Mitigate Respiratory Morbidity in Coronavirus Disease 2019
Protein factor Small molecule Randomized controlled open trial Mixed substance |
Hypoxic patients | In combination with IVIg. Statistically significant improvement in oxygenation, lower rate of progression to mechanical ventilation, and reduced length of hospital stay in patients with alveolar-arterial gradient greater than 200 mm Hg (none of the subjects with lower gradient progressed to mechanical ventilation). Sample size: 16 + 17 control. Dosage: 40 mg daily for 3 days (30 minutes before IVIg infusion). |
Nov/16/2020 | |
|
Low-dose corticosteroid combined with immunoglobulin reverses deterioration in severe cases with COVID-19
Severe severity Small molecule Cohort study |
Patients | 13.49 | In combination with IVIg. Low-dose corticosteroid treatment at the early stage of severe COVID-19 significantly reversed deterioration of clinical status (including respiratory and oxygenation indicators, pulmonary imaging outcomes, markers of inflammation, and other biochemical indicators) and decreased mortality. Sample size: 239 (40 of which were severe). Dosage: 40-80 mg daily for 7-14 days; in more severe cases the initial pulse of up to 160 mg with gradual deescalation upon stabilisation. |
Nov/24/2020 |
|
Successful treatment with methyl-prednisolone pulses for the late phase of COVID-19 with respiratory failure: A single-center case series
Severe severity Small molecule Case series |
Patients with respiratory failure. | 0.79 | Patients with respiratory failure in the late phase of COVID-19 in a small case series might have benefitted from methylprednisolone pulse. Sample size: 4. Dosage: 1000 mg daily for three days. |
Dec/09/2020 |
|
Glucocorticoids with low-dose anti-IL1 anakinra rescue in severe non-ICU COVID-19 infection: A cohort study
Severe severity Small molecule Cohort study |
Severe non-ICU patients | 2.74 | Used with or withour anakinra. Glucocorticoid therapy in severe non-ICU COVID-19 patients was associated with numerical (but not statistical) decrease in death rate. Sample size: 70 (methylprednisolone) + 35 (methylprednisolone + anakinra) + 3 (methylprednisolone + tocilizumab) + 63 control. Dosage: 120 mg daily on days 1-3; 40 mg prednisone equivalent on days 4-10; 20 mg prednisone equivalent on days 11-17; 10 mg prednisone equivalent on days 18-24 . |
Dec/16/2020 |
|
Clinical efficacy of Methylprednisolone and the combined use of Lopinavir/Ritonavir with Arbidol in treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019
Small molecule Cohort study |
Patients | 2.02 | Methylprednisolone use was associated with faster virus negative conversion. Its efficacy was improved if administered no more than 3 days after hospital admission. The length of hospital stay was shorter in patients (having the same daily dose) who received a sub-400 mg cumulative dose. Methylprednisolone in the total cumulative dose of sub-400 mg had only minor effect on physiological and biochemical indexes in severe patients, however. Sample size: 46 (severe to critical) + 10 (mild to moderate) + 3 control (severe to critical) + 15 control (mild to moderate). Dosage: IV injection once or twice a day. Total cumulative dose of 0.75 to 1.5 mg/kg. |
Jan/15/2021 |
|
Early Experience With Methylprednisolone on SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the African American Population, a Retrospective Analysis
ARDS Small molecule Cohort study |
African American Patients with ARDS and acute kidney injury. | 1.26 | Lower mortality and higher odds of renal and pulmonary function improvement in African American patients with ARDS and acute kidney injury (AKI) compared to control. In patients of the lower methylprednisolone dosing subgroup an improvement in renal functions was more frequent compared to the higher dosing subgroup. The same was noted for pulmonary functions. Sample size: 37 + 38 control. Dosage: 1 mg/kg daily (early AKI/ARDS group) or 2 mg/kg daily (late AKI/ARDS group) in two divided IV doses for 3 days, then oral administration (or IV, if oral not possible) over 2 weeks. Endpoint: Survival by day 21 (primary). |
Dec/14/2020 |
|
Tocilizumab plus glucocorticoids in severe and critically COVID-19 patients. A single center experience
IL-6 Severe severity Small molecule Critical severity Antibody Cohort study |
Severe or critical COVID-19 patients | In combination with tocilizumab. The treatment was associated with a significant decrease in markers of inflammation and an increase in lymphocyte counts in critical COVID-19 patients. The observed ratio of severely or critically ill patients who were discharged from hospital (72%) and overall mortality (20%) were considered by the authors to be indicative of the treatment's efficacy. |
Nov/09/2020 | |
|
Methylprednisolone in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia
Severe severity Small molecule Randomized controlled open trial |
Severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients | 1.23 | The planned sample size was not achieved, which might be the reason why an intention-to-treat analysis did not find a significant difference in the primary outcome between the treatment and the control groups. However, per protocol analysis found a significant benefit for the treatment group. Sample size: 35 + 29 control. Dosage: 40 mg twice a day on days 1-3; 20 mg twice a day on days 4-6. Endpoint: Death, ICU admission, or noninvasive ventilation requirement composite (primary). |
Feb/03/2021 |
|
Beneficial effect of combinational methylprednisolone and remdesivir in hamster model of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Small molecule Animal model In vitro |
Monocyte-derived macrophages; golden Syrian hamsters; SARS-CoV-2 strain HKU-001a | 5.78 | Methylprednisolone promoted SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication in human macrophages in vitro and in golden Syrian hamsters' respiratory tracts; however, when used in a hamster model in combination with remdesivir, SARS-CoV-2-related weight loss was prevented and viral loads were decreased. Methylprednisolone alone seemed to dampen inflamation. Attenuated antibody response observed in methylprednisolone monotherapy was not present in this combinational treatment. |
Feb/04/2021 |
|
Benefits of early aggressive immunomodulatory therapy (tocilizumab and methylprednisolone) in COVID-19: Single center cohort study of 685 patients
IL-6 Protein factor Small molecule Antibody Cohort study |
Patients | Corticosteroid treatment was associated with a better overall outcome. Primary endpoind: Need for mechanical ventilation or death. |
Feb/12/2021 | |
|
Corticosteroids and tocilizumab reduce in-hospital mortality in severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a retrospective study in a Spanish hospital
IL-6 Severe severity Small molecule Antibody Cohort study |
Severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients | 2.49 | Alone or combined with tocilizumab. Reduced in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 pneumonia patients. Dosage: 250 mg daily for 3 days (or 120 mg daily if lopinavir/ritonavir was also administered). |
Feb/23/2021 |
|
Effects of Methylprednisolone on Ventilator-Free Days in Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19: A Retrospective Study
ARDS Small molecule Critical severity Cohort study |
ARDS patients | 3.30 | Treated ARDS patients mechanically ventilated at the baseline had statistically significantly more ventilator-free days and shorter length of hospital stay compared to control. There was no significant difference in mortality and more positive blood cultures were detected among patients in the treatment group, however. Sample size: 32 + 45 control. Dosage: 1 mg/kg daily (median) for 5 days (median). Primary outcome: Ventilator-free days within first 28 days. |
Feb/14/2021 |
|
Methylprednisolone or dexamethasone, which one is superior corticosteroid in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a triple-blinded randomized controlled trial
Small molecule Randomized controlled double-blind trial |
Inpatients | 2.69 | A statistically significantly better clinical status, shortened length of hospital stay, and lower need for mechanical ventilation was observed in methylprednisolone-treated patients compared to the dexamethasone-treated ones. Sample size: 44 + 42 dexamethasone control. Dosage: 2 mg/kg/day. Primary outcomes: 28-day mortality and the clinical status on an ordinal scale. |
Apr/10/2021 |
|
Can Anakinra and corticosteroid treatment be an effective option in pregnant women with severe Covid-19?
Protein factor Small molecule Cohort study |
Pregnant patients | 1.74 | A generally good clinical outcome was observed in pregnant patients with COVID-19 treated using anakinra and methylprednisolone. Sample size: 14. Dosage: 80 mg (median) a day for a median duration of 10 days. |
Sep/22/2021 |
|
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults: A rare sequela of SARS-CoV-2 infection
IL-1 Severe severity Protein factor Small molecule Case report Antibody |
A multisystem inflammatory syndrome patient | 3.62 | A patient diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome related to COVID-19 was successfully treated using high-dose methylprednisolone, anakinra, acetylsalicylic acid, and IVIg. Sample size: 1. Dosage: 250 mg every 6 hours. |
May/23/2021 |
|
Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Report on Managing the Hyperinflammation
IL-1 Severe severity Protein factor Children Small molecule Case report Antibody |
A multisystem inflammatory syndrome paediatric patient | 1.44 | A paediatric patient diagnosed with COVID-19-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome was successfully treated using methylprednisolone, anakinra, and IVIg. Sample size: 1. Dosage: 2–10 mg/kg daily, based on clinical status. |
Jan/30/2021 |
|
Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19-associated pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome
RdRpol IL-1 Severe severity Protein factor Children Small molecule Case report Antibody |
A paediatric patient on ECMO | 1.97 | A paediatric patient with severe COVID-19, requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, was successfully treated using methylprednisolone, anakinra, and remdesivir. Sample size: 1. Dosage: 40 mg twice a day for 3 days. |
Jul/09/2020 |
|
MIS-C Treatment: Is IVIG Always Necessary?
Children Small molecule Cohort study |
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome paediatric patients | 3.42 | The results suggest that early methylprednisolone treatment initiation can improve outcomes of COVID-19 paediatric patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome. The analysed treatment protocol includes dosage change and anakinra or IVIg administration upon clinical worsening. Sample size: 31. Dosage: 2–10 mg/kg. |
Nov/03/2021 |
|
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in a 5-year-old
RdRpol IL-1 Protein factor Children Small molecule Critical severity Case report Antibody Mixed substance |
A paediatric patient on ECMO. | 0.69 | A paediatric patient on ECMO was treated with remdesivir, methylprednisolone, IVIg, and anakinra. Sample size: 1. |
Dec/09/2020 |
AI-suggested references
Clinical trials
| ID | Title | Status | Phase | Start date | Completion date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05279482 | Comparison Between Different Doses of Steroids in COVID-19 Patients | Completed | Jan/19/2022 | Mar/09/2022 | |
|
|||||
| NCT04636671 | Methylprednisolone vs. Dexamethasone in COVID-19 Pneumonia (MEDEAS RCT) | Recruiting | Phase 3 | Apr/14/2021 | Oct/01/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04847687 | Investigation of Hospitalisation Times and Mortality According to Drug Dose in Patients Given Systemic Methylprednisolone With a Pre-diagnosis of Covid-19 Pneumonia; Retrospective Study | Completed | Mar/01/2021 | Apr/01/2021 | |
|
|||||
| NCT04559113 | Methylprednisolone in COVID-19 Patients (Methyl19LGH) | Recruiting | Not Applicable | May/01/2020 | Dec/30/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT05133635 | High-Dose Corticosteroid or Tocilizumab for Clinical Worsening of COVID-19 | Withdrawn | Phase 4 | Feb/01/2021 | Apr/01/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04603729 | Comparison of Efficacy of Dexamethasone and Methylprednisolone in Moderate to Severe Covid 19 Disease | Completed | Phase 3 | May/30/2020 | Jul/01/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04341038 | Clinical Trial to Evaluate Methylprednisolone Pulses and Tacrolimus in Patients With COVID-19 Lung Injury | Recruiting | Phase 3 | Apr/01/2020 | Jul/01/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04374071 | Early Short Course Corticosteroids in COVID-19 | Completed | Mar/12/2020 | Apr/30/2020 | |
|
|||||
| NCT05002517 | Randomized, Unicentric, Open, Controlled Clinical Trial, in Phase Iii, to Demonstrate the Effectiveness of Tocilizumab | Active, not recruiting | Phase 3 | Sep/03/2020 | Oct/31/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04349410 | The Fleming [FMTVDM] Directed CoVid-19 Treatment Protocol | Completed | Phase 2|Phase 3 | Apr/11/2020 | Sep/14/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT05047874 | High-dose, Short-term Steroid and Low-dose Long-term Steroid Use in ARDS Caused by COVID-19 | Recruiting | Sep/20/2021 | Oct/30/2021 | |
|
|||||
| NCT04323592 | Methylprednisolone for Patients With COVID-19 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome | Completed | Mar/23/2020 | May/10/2020 | |
|
|||||
| NCT04377503 | Tocilizumab Versus Methylprednisolone in the Cytokine Release Syndrome of Patients With COVID-19 | Not yet recruiting | Phase 2 | May/01/2020 | Nov/01/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04263402 | The Efficacy of Different Hormone Doses in 2019-nCoV Severe Pneumonia | Unknown status | Phase 4 | Feb/01/2020 | Jul/01/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04438980 | Glucocorticoids in COVID-19 (CORTIVID) | Completed | Phase 3 | May/15/2020 | Apr/09/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT05062681 | RCT on the Efficacy of Dexamethasone Versus Methyl Prednisolone in Covid-19 Infected Patients With High Oxygen Flow | Recruiting | Phase 4 | Sep/15/2021 | Mar/15/2022 |
|
|||||
| NCT04273321 | Efficacy and Safety of Corticosteroids in COVID-19 | Completed | Not Applicable | Feb/14/2020 | Apr/15/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04343729 | Methylprednisolone in the Treatment of Patients With Signs of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in Covid-19 | Completed | Phase 2 | Apr/18/2020 | Oct/20/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04988282 | Systemic Corticosteroids in Treatment of Post-COVID-19 Interstitial Lung Disease | Recruiting | Phase 4 | May/24/2021 | Dec/31/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04673162 | Evaluation of the Efficacy of High Doses of Methylprednisolone in SARS-CoV2 ( COVID-19) Pneumonia Patients | Not yet recruiting | Phase 3 | Dec/01/2020 | Jun/01/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04528888 | Steroids and Unfractionated Heparin in Critically Ill Patients With Pneumonia From COVID-19 Infection | Recruiting | Phase 3 | Nov/25/2020 | Jul/30/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04355247 | Prophylactic Corticosteroid to Prevent COVID-19 Cytokine Storm | Recruiting | Phase 2 | Apr/14/2020 | Apr/30/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04499313 | Dexamethasone Vs Methylprednisolone for the Treatment of Patients With ARDS Caused by COVID-19 | Recruiting | Phase 3 | Aug/02/2020 | Nov/30/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04485429 | Efficacy Assessment of Methylprednisolone and Heparin in Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia | Withdrawn | Phase 3 | Jul/20/2020 | Dec/31/2022 |
|
|||||
| NCT04244591 | Glucocorticoid Therapy for COVID-19 Critically Ill Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Failure | Completed | Phase 2|Phase 3 | Jan/26/2020 | Apr/13/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04826588 | Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) in Children With PIMS-TS in Switzerland (SWISSPED-RECOVERY) | Recruiting | Phase 3 | May/23/2021 | Jul/01/2022 |
|
|||||
| NCT04329650 | Efficacy and Safety of Siltuximab vs. Corticosteroids in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia | Recruiting | Phase 2 | Apr/15/2020 | May/20/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04909918 | Impact of Steroids on Inflammatory Response in Covid-19 | Completed | Phase 3 | May/28/2021 | Aug/20/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT03852537 | Steroid Dosing by bioMARker Guided Titration in Critically Ill Patients With Pneumonia | Completed | Phase 2 | Dec/02/2019 | Nov/17/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04780581 | Glucocorticoid Therapy in Coronavirus Disease COVID-19 Patients | Recruiting | Phase 4 | Feb/01/2021 | Dec/31/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04345445 | Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab Versus Corticosteroids in Hospitalised COVID-19 Patients With High Risk of Progression | Not yet recruiting | Phase 3 | Apr/15/2020 | Oct/31/2020 |
|
|||||
