Theaflavin
A flavonoid.
General information
Theaflavin is a natural flavonoid compound with strong antioxidant properties (NCIt).
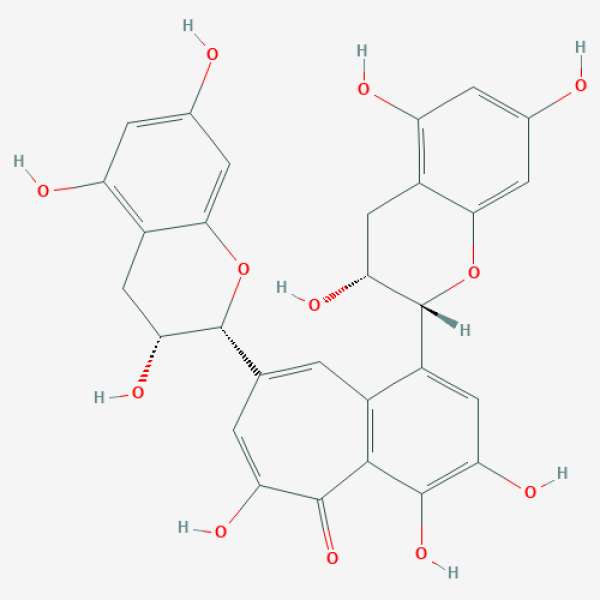
C1[C@H]([C@H](OC2=CC(=CC(=C21)O)O)C3=CC4=C(C(=C(C=C4[C@@H]5[C@@H](CC6=C(C=C(C=C6O5)O)O)O)O)O)C(=O)C(=C3)O)O
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tea Polyphenols EGCG and Theaflavin Inhibit the Activity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Protease In Vitro
3CLpro Small molecule Enzyme assay In vitro |
in vitro enzyme assay; HEK293T (cytotoxicity) | 1.81 | Inhibited the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease in vitro at non-cytotoxic levels. |
Sep/17/2020 |
|
Druggability for COVID-19: in silico discovery of potential drug compounds against nucleocapsid (N) protein of SARS-CoV-2
Nucleocapsid protein Small molecule In silico |
in silico | Predicted to bind the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein. |
Dec/09/2020 |
