Thapsigargin
A sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulu Ca2+ ATPase inhibitor.
General information
Thapsigargin is a natural sesquiterpene lactone. It inhibits Ca2+ ATPase transport of calcium ions into sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum. It is also used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (ChEBI).
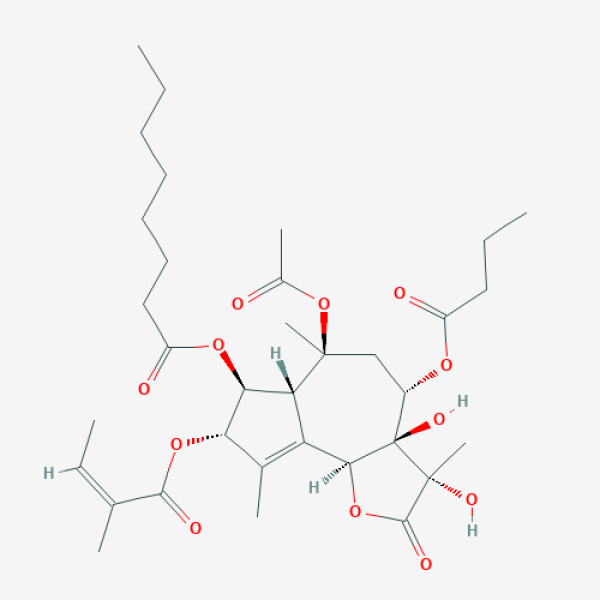
CCCCCCCC(=O)O[C@H]1[C@H]2C(=C([C@@H]1OC(=O)/C(=C\C)/C)C)[C@H]3[C@]([C@H](C[C@]2(C)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)CCC)([C@](C(=O)O3)(C)O)O
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The Host Cell ViroCheckpoint: Identification and Pharmacologic Targeting of Novel Mechanistic Determinants of Coronavirus-Mediated Hijacked Cell States
Preprint |
in silico | one of the top drugs and compounds identified by ViroTreat |
May/17/2020 | |
|
Thapsigargin Is a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Major Human Respiratory Viruses: Coronavirus, Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Influenza A Virus
Small molecule In vitro |
Primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells; Calu-3 cells; Vero E6 cells (contradictory results); SARS-CoV-2 strain 2019-nCoV/Italy-INMI1 | 3.82 | Pre-incubation of primary normal human bronchial cells or Calu-3 cells but not Vero E6 cells with the compound at non-cytotoxic levels lead to SARS-CoV-2 inhibition. This indicates that type I interferon response is necessary for thapsigargin anti-coronaviral activity in vitro. Calu-3 cells pre-incubation with 0.5 µM thapsigargin led to 300-fold and 880-fold decrease of viral progeny production after SARS-CoV-2 infection and SARS-CoV-2/H1N1 influenza virus coinfection, respectively. |
Feb/03/2021 |
AI-suggested references
| Link | Publication date |
|---|---|
|
Emergent SARS-CoV-2 variants: comparative replication dynamics and high sensitivity to thapsigargin
|
Nov/19/2021 |
