Nafamostat mesylate
A serine protease inhibitor.
General information
Nafamostat mesylate is inhibits a broad-spectrum of serine proteases. It has anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, mucus clearing, and potential antiviral activities. Nafamostat mesylate might inhibit the activity of transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2), which mediates viral cell entry for SARS-CoV-2, thereby inhibiting viral infection (NCIt).
Nafamostat mesylate on DrugBank
Nafamostat mesylate on PubChem
Nafamostat mesylate on Wikipedia
Marketed as
BERABU; BUIPEL; BUSERON; COAHIBITOR; FAMOSET; FUTHAN; NAFASTON; NAFATAT; NAMOSTATT; NAOTAMIN; OPSUN; PATHRON; RONASTAT
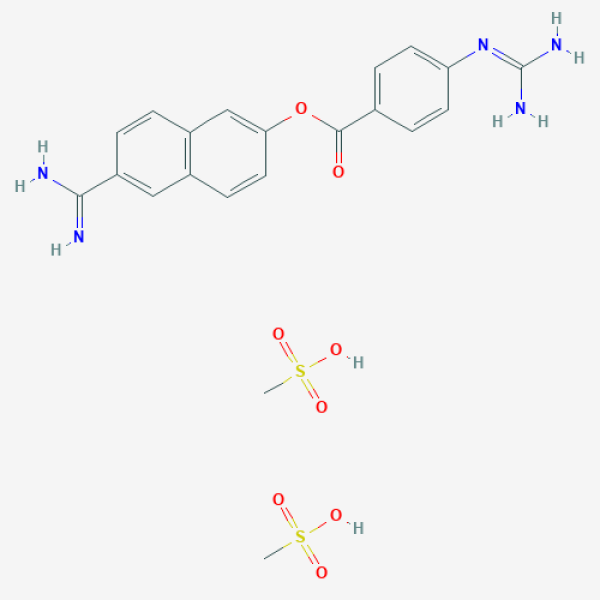
CS(=O)(=O)O.CS(=O)(=O)O.C1=CC(=CC=C1C(=O)OC2=CC3=C(C=C2)C=C(C=C3)C(=N)N)N=C(N)N
Supporting references
AI-suggested references
Clinical trials
| ID | Title | Status | Phase | Start date | Completion date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04418128 | Clinical Efficacy of Nafamostat Mesylate for COVID-19 Pneumonia | Not yet recruiting | Phase 2|Phase 3 | Jun/10/2020 | Apr/30/2021 |
|
|||||
