Fluoxetine
A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
General information
Fluoxetine is a diphenhydramine selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. It has antidepressant, anti-anxiety, anti-obsessional, and anti-bulimic properties. It could also suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, which would be beneficial for cytokine storm management (NCIt).
Fluoxetine on DrugBank
Fluoxetine on PubChem
Fluoxetine on Wikipedia
Synonyms
Prozac
Marketed as
ADOFEN; ANIMEX-ON; FLUOXEREN; FLUOXETINE; FLUOXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE; FONTEX; LADOSE; PROZAC; SARAFEM
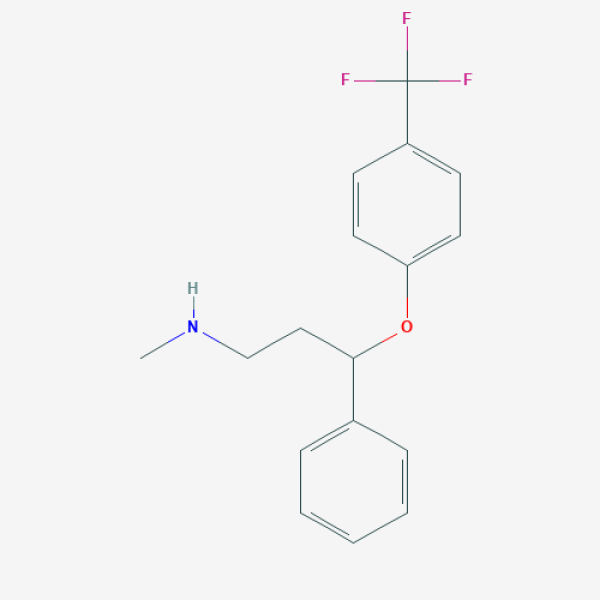
CNCCC(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(F)(F)F
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sphingolipid Biosynthesis Inhibition As A Host Strategy Against Diverse Pathogens
Preprint |
Theory only | molecular function highly similar to chloroquine |
Apr/14/2020 | |
|
The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2
Preprint |
VERO cells | Fluoxetine treatment resulted in a decrease in viral protein expression. |
Jun/14/2020 | |
|
Dual Targeting of 3CLpro and PLpro of SARS-CoV-2: A Novel Structure-Based Design Approach to treat COVID-19
3CLpro RdRpol Small molecule In silico |
in silico | Predicted to bind both the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and 3C-like protease. |
Dec/10/2020 | |
|
The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue
Small molecule In vitro |
Vero cells; human lung tissue | 4.00 | The drug inhibited SARS-CoV-2 with an EC50 of 387 ng/ml in Vero cells. It displayed antiviral activity in human lung tissue ex vivo. The R-stereoisomer, which is not the dominant serotonin reuptake inhibitor, showed efficacy, as well. |
Mar/15/2021 |
AI-suggested references
Clinical trials
| ID | Title | Status | Phase | Start date | Completion date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05283954 | Use of a Combined Regimen of Fluoxetine, Prednisolone and Ivermectin in the Treatment of Mild COVID-19 to Prevent Disease Progression Progression in Papua New Guinea | Not yet recruiting | Phase 2|Phase 3 | May/01/2022 | Jul/30/2022 |
|
|||||
| NCT04377308 | Fluoxetine to Reduce Intubation and Death After COVID19 Infection | Recruiting | Phase 4 | May/01/2020 | Oct/20/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04780152 | TDCS in Pediatric and Teenage Patients With Major Depressive Disorder During COVID-19 Pandemic | Recruiting | Phase 2|Phase 3 | Oct/01/2021 | Sep/01/2022 |
|
|||||
| NCT04570449 | Fluoxetine to Reduce Hospitalization From COVID-19 Infection (FloR COVID-19) | Withdrawn | Early Phase 1 | Nov/01/2020 | Dec/01/2021 |
|
|||||
