Deguelin
A rotenone derivative.
General information
Deguelin is a natural rotenoid with anticancer properties. It was shown to reduce malignant transformation and tumour cell propagation and to enhance apoptosis. Deguelin interacts with multiple oncogenic signalling pathways (Varughese et al., 2019). It displayed anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties in vitro, which might root from its ability to bind ATP-binding site of DDX42 helicase, a host RNA-binding protein predicted to interact with SARS-CoV-2 RNA (Sun et al., 2021).
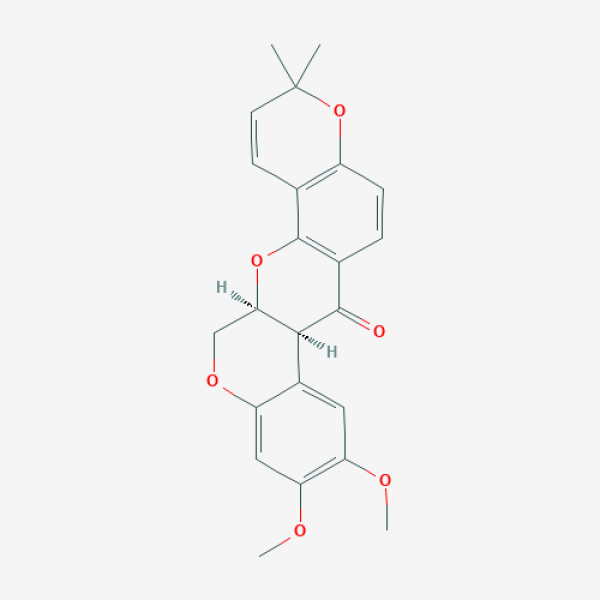
CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2O[C@@H]4COC5=CC(=C(C=C5[C@@H]4C3=O)OC)OC)C
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In vivo structural characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome identifies host proteins vulnerable to repurposed drugs
RNA Biophysical assay In vitro Mechanism In silico |
in silico; in vitro biophysical assay; Caco-2 cells; Huh7.5.1 cells; Calu-3 cells; A549-ACE2 cells | 38.64 | Inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection in Huh7.5.1 cells with low cytotoxicity. Antiviral activity was observed in Caco-2 and Calu-3 cells (but not in A549-ACE2 cells), as well. Its activity might root from its ability to bind ATP-binding site of DDX42 helicase, which is a host RNA-binding protein predicted to interact with SARS-CoV-2 RNA. |
Feb/09/2021 |
AI-suggested references
| Link | Publication date |
|---|---|
|
Natural Products, Alone or in Combination with FDA-Approved Drugs, to Treat COVID-19 and Lung Cancer.
|
Jun/18/2021 |
