Camostat mesylate
A serine protease inhibitor.
General information
Camostat (mesylate) is a serine protease inhibitor. It has anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and potential antiviral activities (NCIt). Data of Ou et al. (2021) suggets that camostat blocks TMPRSS2 mediated viral entry at the cell membrane but does not impede TMPRSS2 mediated entry in endosomes.
Camostat mesylate on DrugBank
Camostat mesylate on PubChem
Camostat on Wikipedia
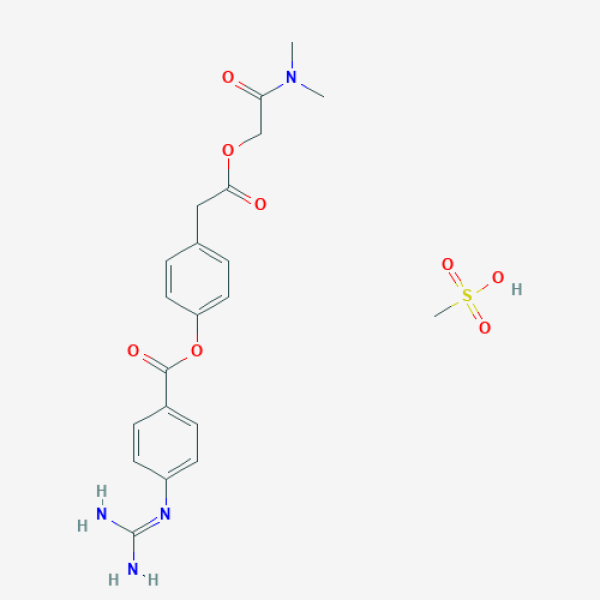
CN(C)C(=O)COC(=O)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N=C(N)N.CS(=O)(=O)O
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The anticoagulant nafamostat potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro: an existing drug with multiple possible therapeutic effects
Preprint |
lung epithelium-derived Calu-3 cells | 10-fold less active than nafamostat mesylate |
Apr/23/2020 | |
|
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin is an Inhibitor of the SARS-CoV2-Priming Protease TMPRSS2
TMPRSS2 Preprint |
HEK-293T cell culture | inhibited TMPRSS2 proteolytic function |
Oct/07/2020 | |
|
Generation of human bronchial organoids for SARS-CoV-2 research
Preprint |
human bronchial organoids | May/26/2020 | ||
|
A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing
Small molecule |
in silico | 42.78 | Apr/30/2020 | |
|
SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV differ in their cell tropism and drug sensitivity profiles
Preprint |
CaCo-2 cells | limited activity |
Apr/05/2020 | |
|
An Enzymatic TMPRSS2 Assay for Assessment of Clinical Candidates and Discovery of Inhibitors as Potential Treatment of COVID-19
Preprint |
in vitro | Jun/23/2020 | ||
|
Computational drug re-purposing targeting the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 as an effective strategy to neutralize COVID-19
Spike protein Small molecule In silico |
in silico | 3.26 | Predicted to bind the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD. |
Nov/06/2020 |
|
Hydroxychloroquine-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry is attenuated by TMPRSS2
Spike protein TMPRSS2 Cathepsin L In vitro Mechanism |
hACE2-HEK293T cells; hACE2-H1299 cells; hACE2-H1975 cells; Vero cells; Calu-3 cells; SARS-CoV-2 S pseudovirus | 6.22 | Acts synergistically with <a href= |
Jan/19/2021 |
|
Spontaneous binding of potential COVID-19 drugs (Camostat and Nafamostat) to human serine protease TMPRSS2
TMPRSS2 Small molecule In silico |
in silico | 6.02 | Predicted to bind the active site of the TMPRSS2 protease (with less specificity than nafamostat). |
Dec/28/2020 |
|
SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and P.1 escape from neutralizing antibodies
Spike protein RNA Small molecule Peptide In vitro Antibody Mixed substance |
Caco-2 cells; Vero cells; Sera of vaccinated individuals; (VSV) SARS-CoV-2 Spike-pseudotyped virus (WT, B.1.1.7, B.1.351, ant P.1 variants) | 38.64 | Camostat displayed in vitro inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-pseudotyped virus infection for all tested emergent Spike variants (B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1). |
Mar/20/2021 |
|
Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-Cov-2
Small molecule In vitro Screening |
Huh7.5 cells; Calu-3 cells; primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells; iPSC-derived AT2 cells; SARS-CoV-2 strain USA WA1/2020 | 8.11 | Camostat inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection in Calu-3 cells but not in Vero or Huh7.5 cells. |
Mar/23/2021 |
|
Structure-based phylogeny identifies Avoralstat as a TMPRSS2 inhibitor that prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice
Small molecule Enzyme assay Peptide Animal model In vitro In silico |
in silico; in vitro enzyme assay; Calu-3 2B4 cells; hACE2-BALB/c mice; (VSV) SARS-CoV-2 Spike pseudovirus; SARS-CoV-2 live virus | 11.86 | Camostat mesylate inhibited TMPRSS2 in vitro with an IC50 of ca. 1.01 nM. It inhibited pseudoviral entry in Calu-3 cells with an EC50 of ca. 0.7 μM. The compound significantly reduced viral replication in cell culture (more than a ten-fold decrease in viral RNA signal with a 1 μM dose). It significantly reduced lung viral loads in mice after a viral challenge. |
Apr/12/2021 |
AI-suggested references
Clinical trials
| ID | Title | Status | Phase | Start date | Completion date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04353284 | Camostat Mesylate in COVID-19 Outpatients | Completed | Phase 2 | Jun/09/2020 | Apr/22/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04435015 | The Utility of Camostat Mesylate in Patients With COVID-19 Associated Coagulopathy (CAC) and Cardiovascular Complications | Not yet recruiting | Phase 1|Phase 2 | Nov/01/2021 | Dec/31/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04355052 | Open Label Study to Compare Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Hydroxychloroquine Combined With Azithromycin Compared to Hydroxychloroquine Combined With Camostat Mesylate and to "no Treatment" in SARS CoV 2 Virus | Recruiting | Phase 3 | Apr/11/2020 | Dec/11/2020 |
|
|||||
| NCT04608266 | CAMOVID : Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Camostat Mesylate for the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection - COVID-19 in Ambulatory Adult Patients | Terminated | Phase 3 | Dec/03/2020 | Dec/02/2021 |
|
|||||
| NCT04681430 | Reconvalescent Plasma/Camostat Mesylate Early in SARS-CoV-2 Q-PCR (COVID-19) Positive High-risk Individuals | Completed | Phase 2 | Jan/08/2021 | Oct/29/2021 |
|
|||||
