Amiodarone
A benzofurane antiarrhythmic agent.
General information
Amiodarone is a benzofuran derivative rich in iodine with antiarrhythmic and vasodilatory properties. It blocks multiple ion channels in cardiac tissue and inhibits alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors (NCIt).
Amiodarone on DrugBank
Amiodarone on PubChem
Amiodarone on Wikipedia
Marketed as
As AMIODARONE HYDROCHLORIDE: CORDARONE; NEXTERONE; PACERONE
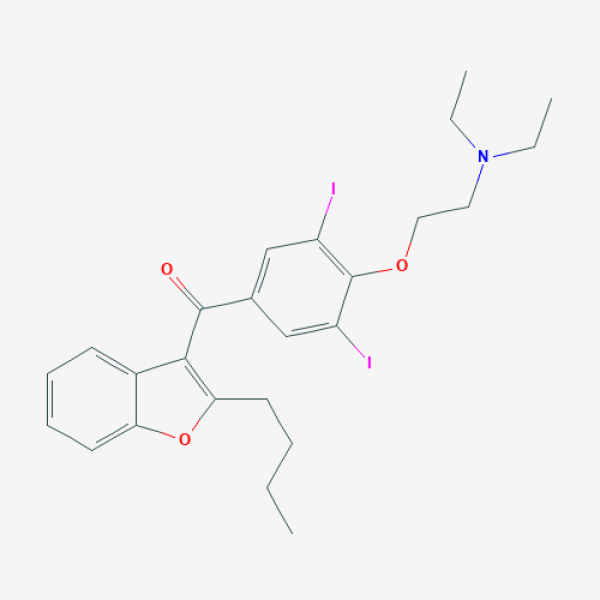
CCCCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2O1)C(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3)I)OCCN(CC)CC)I
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sphingolipid Biosynthesis Inhibition As A Host Strategy Against Diverse Pathogens
Preprint |
Theory only | molecular function highly similar to chloroquine |
Apr/14/2020 | |
|
Morphological Cell Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Identifies Drug Repurposing Candidates for COVID-19
Preprint |
Huh7 cells | May/27/2020 | ||
|
Oral drug repositioning candidates and synergistic remdesivir combinations for the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19
Preprint In vitro Screening |
HeLa-ACE2 cells | Jun/16/2020 | ||
|
Safety and Efficacy of Amiodarone in a Patient With COVID-19
Small molecule Case report |
Patient | Treatment resulted in clinical improvement. Sample size: 1. Dosage: 15-mg/kg/24 h intravenous infusion on day 1, followed by the oral administration of 400 mg twice daily (0.55 μg/ml in serum on day 3). |
May/29/2020 | |
|
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs
Small molecule In vitro Screening |
Huh-7 cells (pseudovirus-based assay); Vero E6 cells (antiviral activity); SARS-CoV-2 (WIV04) | 5.06 | Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 spike protein pseudovirus cell entry and significally inhibits viral replication in vitro. |
Oct/28/2020 |
