Abacavir
nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitor
General information
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor analog of guanosine, which is phosphorylated to active metabolites that compete for incorporation into viral DNA. They inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme competitively and act as a chain terminator of DNA synthesis. Abacavir was approved for the use in USA in 1998. It is used in combination with other agents in the therapy of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It decreases HIV viral loads, retartds or prevents the damage to the immune system, and reduces the risk of developing AIDS.
Regarding SARS-CoV-2, our AIM tool found the data that abacavir could help against SARS-CoV-2 by inhibiting its replication.
Abacavir on PubChem
Abacavir on DrugBank
Abacavir on Wikipedia
Synonyms
abacavir sulfate
Marketed as
ZIAGEN®
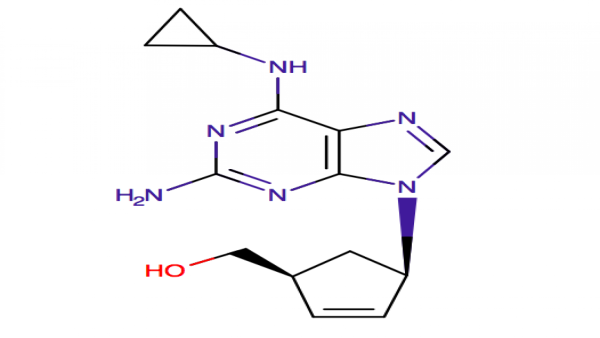
C14H18N6O
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Predicting commercially available antiviral drugs that may act on the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Wuhan, China through a drug-target interaction deep learning model
Preprint In silico |
in silico | Feb/02/2020 | ||
|
Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
|
in silico | Feb/22/2020 |
