25-hydroxycholesterol
An enzymatic product of cholesterol 25-hydroxylase.
General information
25-hydroxycholesterol is a human cholesterol metabolite. Upon viral infection type I and II interferons are induced and cholesterol 25-hydroxylase CH25H expression increases. 25-hydroxycholesterol treatment in vitro leads to acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase activation, which in turn depletes cholesterol on the plasma membrane. This inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry at the level of membrane fusion (Wang et al., 2020).
25-hydroxycholesterol on DrugBank
25-hydroxycholesterol on PubChem
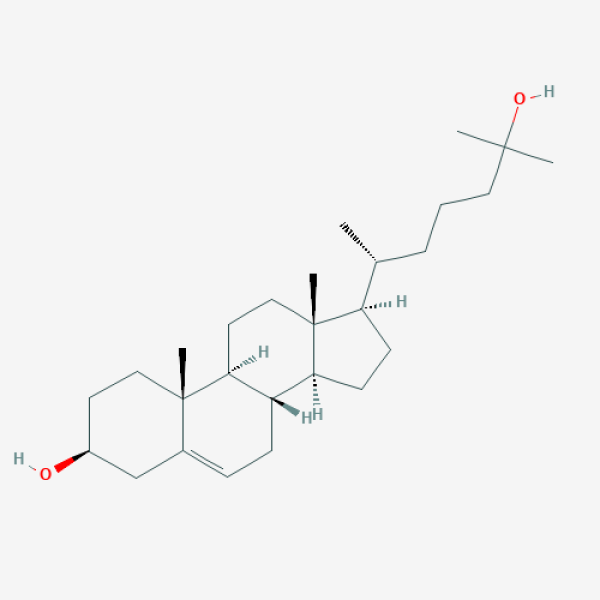
C[C@H](CCCC(C)(C)O)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]2[C@@]1(CC[C@H]3[C@H]2CC=C4[C@@]3(CC[C@@H](C4)O)C)C
Supporting references
| Link | Tested on | Impact factor | Notes | Publication date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking membrane fusion
Small molecule In vitro |
Vero E6 cells; HEK293 cells; HEK293-hACE2 cells; MA104 cells; primary human intestinal epithelial cells; cardiomyocytes | 9.41 | 25-hydroxycholesterol (25HC) potently inhibits the early stage of SARS-CoV-2 (chimeric) infection in vitro. 25HC inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection likely at the level of S protein-mediated fusion. Antiviral activity of 25HC was observed to be dose-dependent. |
Nov/25/2020 |
|
25-Hydroxycholesterol is a potent SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor
Small molecule Animal model |
Vero E6 cells; mice; SARS-CoV-2 mouse-adapted strain MASCp6 | 20.51 | Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro and significantly reduced viral RNA load in an animal model (potentially blocking the viral entry into cells). |
Aug/18/2020 |
|
Cholesterol 25‐Hydroxylase inhibits SARS‐CoV‐2 and other coronaviruses by depleting membrane cholesterol
Small molecule In vitro Mechanism |
Calu‐3 and Caco‐2 cells; A549‐ACE2 cells (RNA-seq analyses); human lung organoids; bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (RNA-seq analyses); SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped virus; SARS‐CoV-2 strain USA‐WA1/2020 | 9.96 | Upon viral infection type I and II interferons are induced and cholesterol 25u2010hydroxylase CH25H expression increases. 25-hydroxycholesterol treatment in vitro leads to acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase activation, which in turn depletes cholesterol on the plasma membrane. This inhibits viral entry at the level of membrane fusion. |
Sep/18/2020 |
